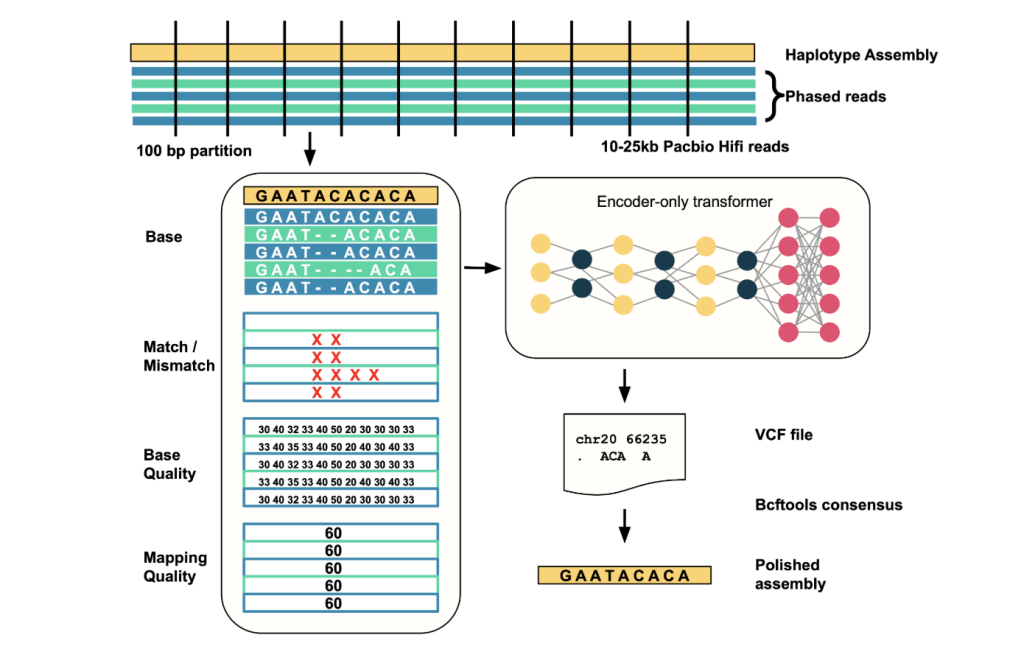
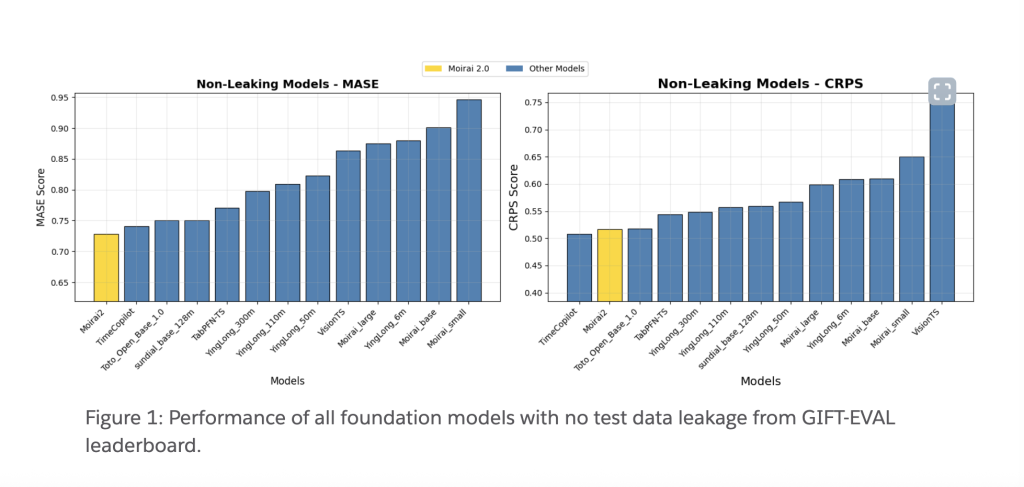
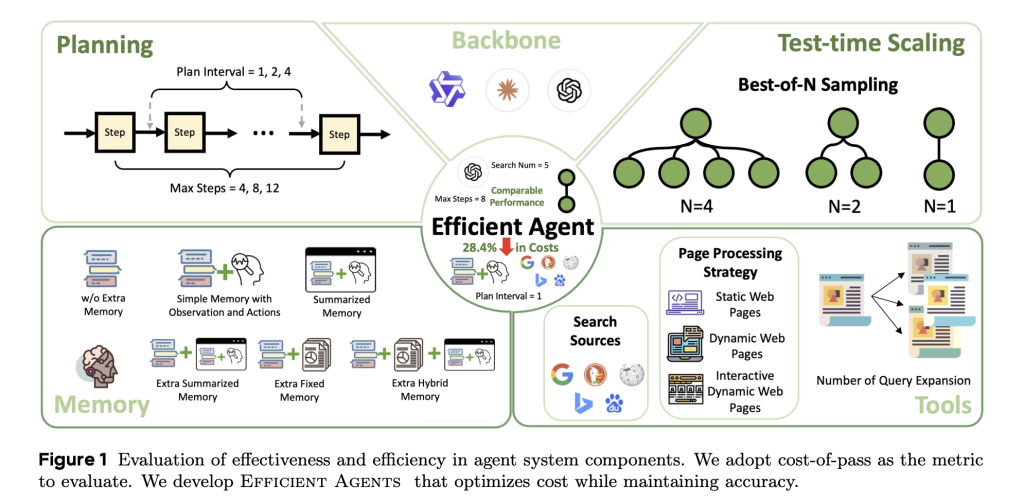
NVIDIA XGBoost 3.0: Training Terabyte-Scale Datasets with Grace Hopper Superchip
NVIDIA has unveiled a major milestone in scalable machine learning: XGBoost 3.0, now able to train gradient-boosted decision tree (GBDT) models from gigabytes up to 1 terabyte (TB) on a single GH200 Grace Hopper Superchip. The breakthrough enables companies to process immense datasets for applications like fraud detection, credit risk modeling, and algorithmic trading, simplifying the once-complex process of scaling machine learning ML pipelines.
Breaking Terabyte Barriers
At the heart of this advancement is the new External-Memory Quantile DMatrix in XGBoost 3.0. Traditionally, GPU training was limited by the available GPU memory, capping achievable dataset size or forcing teams to adapt complex multi-node frameworks. The new release leverages the Grace Hopper Superchip’s coherent memory architecture and ultrafast 900GB/s NVLink-C2C bandwidth. This enables direct streaming of pre-binned, compressed data from host RAM into the GPU, overcoming bottlenecks and memory constraints that previously required RAM-monster servers or large GPU clusters.
Real-World Gains: Speed, Simplicity, and Cost Savings
Institutions like the Royal Bank of Canada (RBC) have reported up to 16x speed boosts and a 94% reduction in total cost of ownership (TCO) for model training by moving their predictive analytics pipelines to GPU-powered XGBoost. This leap in efficiency is crucial for workflows with constant model tuning and rapidly changing data volumes, allowing banks and enterprises to optimize features faster and scale as data grows.
How It Works: External Memory Meets XGBoost
The new external-memory approach introduces several innovations:
- External-Memory Quantile DMatrix: Pre-bins every feature into quantile buckets, keeps data compressed in host RAM, and streams it as needed, maintaining accuracy while reducing GPU memory load.
- Scalability on a Single Chip: One GH200 Superchip, with 80GB HBM3 GPU RAM plus 480GB LPDDR5X system RAM, can now handle a full TB-scale dataset—tasks formerly possible only across multi-GPU clusters.
- Simpler Integration: For data science teams using RAPIDS, activating the new method is a straightforward drop-in, requiring minimal code changes.
Technical Best Practices
- Use
grow_policy='depthwise'for tree construction for best performance on external memory. - Run with CUDA 12.8+ and an HMM-enabled driver for full Grace Hopper support.
- Data shape matters: the number of rows (labels) is the main limiter for scaling—wider or taller tables yield comparable performance on the GPU.
Upgrades
Other highlights in XGBoost 3.0 include:
- Experimental support for distributed external memory across GPU clusters.
- Reduced memory requirements and initialization time, notably for mostly-dense data.
- Support for categorical features, quantile regression, and SHAP explainability in external-memory mode.
Industry Impact
By bringing terabyte-scale GBDT training to a single chip, NVIDIA democratizes access to massive machine learning for both financial and enterprise users, paving the way for faster iteration, lower cost, and lower IT complexity.
XGBoost 3.0 and the Grace Hopper Superchip together mark a major leap forward in scalable, accelerated machine learning.
Check out the Technical details. Feel free to check out our GitHub Page for Tutorials, Codes and Notebooks. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 100k+ ML SubReddit and Subscribe to our Newsletter.
The post NVIDIA XGBoost 3.0: Training Terabyte-Scale Datasets with Grace Hopper Superchip appeared first on MarkTechPost.
MarkTechPost


![Proxy Servers Explained: Types, Use Cases & Trends in 2025 [Technical Deep Dive]](https://www.marktechpost.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/a-clean-minimalist-diagram-illustrating-_9aCHlNyfQymMdgxTzJO73A_SCH0U_uISCeZb6TJycAZiA-1-1024x574.png)